Category : Gastroenterology
In recent years, gut health has emerged as a key area of focus in nutritional science and holistic wellness. Our digestive system, often underestimated, is a complex ecosystem crucial to our overall health. As research deepens, the link between gut health and various aspects of our well-being becomes increasingly clear, underscoring the importance of nurturing this vital system.
What is Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse community of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract. Comprised mainly of bacteria but also includes fungi, viruses, and other microbes, it forms a complex ecosystem essential for human health. There are about 100 trillion bacteria, both good and bad, live inside our digestive system. These microbes have tremendous potential to influences everything from digestion to mental health.
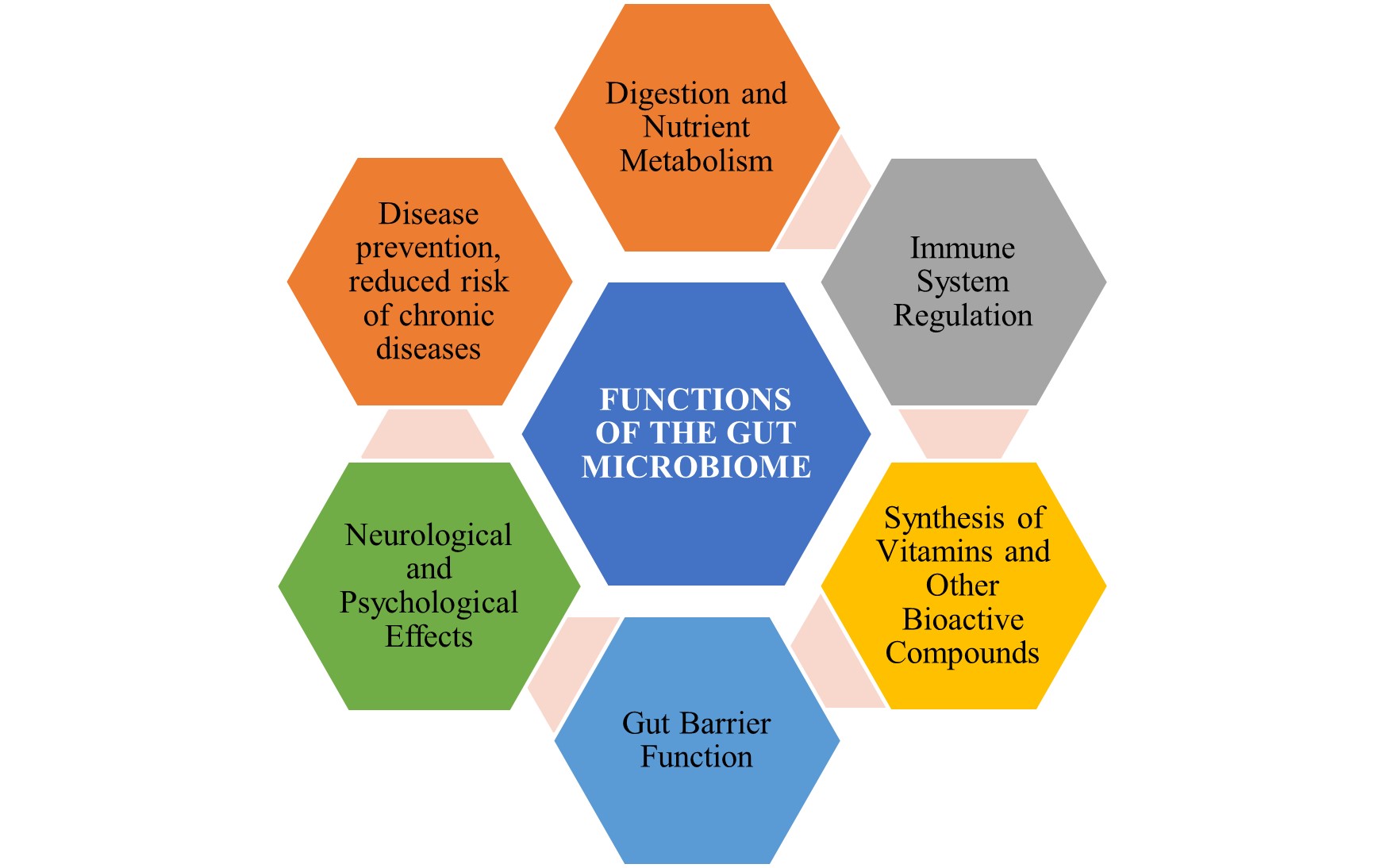
Role of gut microbiome in health
- Inflammatory Conditions.
- Antibiotic Resistance.
- Mental health connection.
Here are some Gut-Healthy Foods
-
Probiotics: Incorporating probiotic-rich foods into your diet can help introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut. These bacteria support gut health by replenishing and maintaining the microbiome. Foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables (sauerkraut, kimchi) are excellent sources.

- Prebiotics: These non-digestible fibres feed beneficial gut bacteria, helping them thrive. Incorporate foods like garlic, onions, oats, bananas, and apples into your diet to boost prebiotic intake.
-
High-Fiber Foods: Dietary fibre supports regular bowel movements and feeds healthy gut bacteria. Whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables are rich in fibre and beneficial for gut health.

- Fermented Foods: It contains beneficial bacteria produced during the fermentation process, which can help improve gut health. Incorporate fermented foods such as yogurt, idli, dosa, vada, dhokla, curd, ragi ambali, pickled vegetable, uthappam, Adai, kimchi, sauerkraut and tempeh etc into your diet regularly.


-
Polyphenol-Rich Foods: Polyphenols, found in foods like berries, nuts, dark chocolate and green tea, have antioxidant properties that support gut health by reducing inflammation and encouraging the growth of good bacteria.


Therefore, maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through diet, lifestyle, and targeted interventions is important for overall digestive health and well-being.
“A healthy gut is the foundation of a healthy body and mind. To understand how your body works, you must first understand how your gut works”
Pooja. G
Dietician