Category : Rheumatology
Gout is a painful arthritis type that is triggered by an abnormal amount of uric acid in the body. When uric acid builds up, it crystallizes in the joints in the shape of needles, causing extreme pain and inflammation. This article seeks to provide answers for some of the frequent queries that people have about gout, its reasons, symptoms, treatment, and which foods to eat.
- What Causes Gout?
Gout occurs when there is too much uric acid in the blood. Causes or factors that contribute to a person having gout include:- Kidney Dysfunction: Failing kidneys that cannot excrete uric acid.
- High-purine Diet: Increased intake of red meats, seafood, and alcohol leads to excess uric acid production.
- Obesity: Putting on unnecessary pounds leads to more uric acid production.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Kidney disease, diabetes, and hypertension can all contribute.
- Certain Medications: Some cancer therapies, diuretics, and aspirin can lead to elevated uric acid levels.
- What Are The Symptoms Of Gout?
A gout attack comes rapidly and without warning and is characterized by:- Severe Joint Pain: Joints both in the big toe and knees and even the ankles and fingers can all be affected.
- Redness and Swelling: Inflamed and tender joints tend to swell and turn red in color.
- Changes in Skin: The area surrounding the joint may look smoother than usual and feel significantly warmer.
- Restriction in Movement: The patient can experience pain and suffer from swelling due to restriction in skin and joint function.
- A physician may decide if a person has gout through: – Analysis of joint’s fluid: Taking out fluid from the joint in order to Wallet thin thickness measures B3 and B5 in milliliters.
- How is Gout Diagnosed?
A physician is able to diagnose gout thanks to the following:Joint fluid analysis: Taking out a sample of the joint fluid to check for urate crystals.Blood tests: Checking for the concentration of uric acid in the blood (even though some gout sufferers with normal uric acids levels may have it). Imaging tests: Ulrasound and X-rays can detect crystal formations as well as other evidence of chronic arthritis. - What Are The Treatment Options Available?
Treatment aims at: Acute Attack Relief: Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) which include ibuprofen or naproxen.Reduce the inflammatory response using colchicines. Severe pain may require oral or injectable corticosteroids. Long-Term Management: Drugs such as allopurinol or febuxostat that increase the excretion of uric acid. Dietary changes include losing weight, eating healthy, and lowering alcohol consumption. - What Are Some Self-Help Measures?
Keep well hydrated: Drinking lots of water helps to remove uric acid from the body. Exercise regularly: Helps maintain a healthy body weight. Refrain from alcohol and soft drinks containing sugar: These substances may lead to a flare-up. During a gout attack, use ice packs on the affected areas to lessen inflammation. Follow the medication as prescribed by your health care provider. - Which Foods Need To Be Cut Down On Or Eliminated Entirely?
In the table below, foods which need to be eliminated or restricted, and encouraged for gout management are shown.
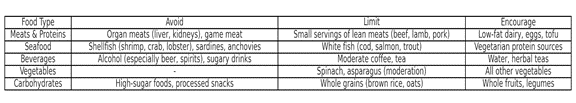
- Steps in Prevention of Gout Attacks
Look out for two different categories of prevention measures:- Medical help: People suffering from frequent attacks can be prescribed gout medications.
- Lifestyle change: Staying active with the exercise as well as maintaining a healthy diet could be preventative measures in eating low purine foods.
- Although it is different to abstain from alcohol and smoking it can also be helpful in avoiding the triggers.
- Prognosis of The Condition
Gout is a chronic ailment, but it is manageable with the right treatment. The very first and foremost step is to look for diagnosis and alter your way of living. That alone can impede on joint abrasion and inflamation of the bone. However, neglecting treatments will result in uric crystal deposits under the skin and joint changes.
Reasoning Towards The Conclusion:
Gout becomes very painful over a longer period of time and requires treatment. It is essential for clients to consult professionals when they notice first signs of gout. It does not grow worse overnight, making it easy to treat with dietary restrictions and medications.
For further information:
Dr. Mahabaleshwar Mamadapur,
Dept Of Clinical Immunology and Rheumatology,
JSS Hospital, Mysore